INFORMATION AVAILABLE IN ENGLISH, GUJARATI AND HINDI
The tonsils are areas of tissue on both sides of the throat, at the back of the mouth. Your child’s tonsils help them to build up immunity and fight infection. In many children, the tonsils become repeatedly infected with bacteria and viruses, which make them swell and become painful. This is called tonsillitis.
What causes tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is the word used when the tonsils are infected so swell and become painful. Both bacteria and viruses can cause an infection – these are usually picked up as part of everyday life so there is little you can do to prevent them although good hygiene including hand washing is important.
What are the signs and symptoms of tonsillitis?
The main symptom of tonsillitis is a sore throat, which is particularly painful when swallowing. Your child may complain of earache as well.
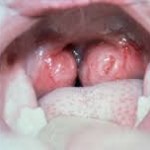
The tonsils may also have a white covering or spots, which are a sign that the body is fighting off the infection. Your child’s neck may look a little swollen as well, and they may have a temperature.
How is tonsillitis diagnosed?
Tonsillitis can be diagnosed by looking closely in the mouth, sometimes using a small torch to look at the back of the mouth.
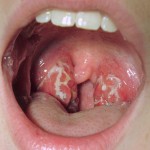
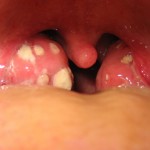 Acute Tonsillitis with pus
Acute Tonsillitis with pus
How is tonsillitis treated?
Pain relief medicines, such as paracetamol and ibuprofen can help reduce the pain and also bring down a temperature. If the infection was caused by a bacteria, the child will require antibiotics. Most cases of tonsillitis disappear within a few days.
If your child has repeated bouts of tonsillitis, we may suggest an operation to remove the tonsils.
SURGERY FOR TONSILLS AND ADENOIDS
The tonsils and adenoids are areas of tissue at the back of the throat. The tonsils are on both sides of the throat, at the back of the mouth, and are clearly visible. Adenoids are not visible, as they are high in the throat behind the nose.
Your child’s tonsils and adenoids help him or her to build up immunity and fight infection. Adenoids and tonsils seem to grow during childhood and then shrink around the age of four. By the time your child reaches adulthood, his or her adenoids and tonsils will have disappeared almost completely. This is because they are no longer needed, as your child’s body will have other defence mechanisms to fight against infection.
Why do tonsils have to be removed?
In many children, the tonsils become repeatedly infected with bacteria and viruses, which make them swell and become painful. Removing your child’s tonsils and adenoids will solve these problems.
Your child may have larger than average tonsils and adenoids, which partially block his or her airway. This can make it difficult for them to breathe through their nose. As a result, your child may breathe through their mouth and snore loudly when asleep. This can lead to a condition called sleep apnoea, where your child stops breathing for a couple of seconds while asleep and then starts again. This can severely disturb their sleep.
There is also a link between large tonsils and adenoids and a condition called glue ear. This happens when the middle ear becomes blocked by a sticky substance which affects your child’s hearing.
What are the risks of this operation?
Every operation carries some risk of infection but we will often give your child antibiotics as a precaution.
The risk of bleeding is usually greatest in the first few days after this operation. It is rarely serious.
Are there any alternatives to this operation?
If your child is having difficulties in breathing or has developed glue ear, it is probably better to have his or her tonsils and adenoids removed.
When your child gets home
Your child will probably feel uncomfortable for a week after the operation and may find swallowing difficult. They may also be reluctant to eat certain foods or brush their teeth.
GUJARATI
ટોન્સીલ :
ગળામાં જીભની પાછળ ડાબી અને જમણી બાજુ ટોન્સીલ(કાકડાં) આવેલાં હોય છે. બાળકોમાં ટોન્સીલનું ઇન્ફેક્શન સામાન્ય છે અને યોગ્ય એÂન્ટબાયોટીકથી મટાડી શકાય છે. વારંવાર ટોન્સીલમાં ઇન્ફેક્શનથી બાળકોની તંદુરસ્તી જાખમાતી હોય તો આૅપરેશન કરવાવું જરૂરી થાય છે, જે સામાન્ય રીતે બાળક ૪ વર્ષનું થાય પછી કરાવવું.
એડીનોઇડસ :
એડીનોઇડસ(નાકની પાછળના મસા) પણ નાના-નાના ટોન્સીલ જ છે જે નાકની પાછળમાં થતા હોય છે. તેમાં વારંવાર ઇન્ફેક્શન થવાથી તે મોટા થાય છે, જેથી બાળકને નાકથી શ્વાસ લેવાતો નથી. બાળક મોઢું ખુલ્લું રાખી શ્વાસ લે છે અને રાત્રે ઊંઘમાં નસકોરાં બોલાવે છે. આથી બાળકને મોઢાંમાંથી વાસ પણ આવે. એડીનોઇડ્સનું આૅપરેશન ૨ વર્ષ પછી કરાવી શકાય. ઘણીવાર આ આૅપરેશન કાકડા સાથે પણ કરવામાં આવે છે. •
HINDI
टॉन्सिल और एडीनोइड्स
टॉन्सिल, गले के भीतर जीभ के पीछे दाई और बाई ओर होता हैं। बच्चों में टॉन्सिल का संक्रमण एक आम बात है और उचित एंटीबायोटिक से इसे ठीक किया जा सकता है। लेकिन बार-बार टॉन्सिल के संक्रमण के कारण यदि बच्चे के स्वास्थ में जोखिम हो तो ऑपरेशन कराना आवश्यक हो जाता है। सामान्यतः यह ऑपरेशन बच्चे के ४ वर्ष का हो जाने के बाद किया जाना चाहिए।
एडीनोइड्स – नाक के पीछे छोटे-छोटे टॉन्सिल या एक प्रकार का मसा है। इनमें बार-बार संक्रमण होने पर यह बड़े हो जाते है। इस कारण बच्चा नाक के द्वारा श्वास नहीं ले सकता है। बच्चा मुँह खोलकर श्वास लेता है और रात में नींद में खर्राटें भरता है। इस कारण बच्चे के मुँह से दुर्गंध भी आती है। एडीनोइड्स का ऑपरेशन २ वर्ष की आयु के बाद किया जा सकता है। कई बार यह ऑपरेशन टॉन्सिल के साथ किया जाता है। •