Heel bone
Your heel bone (or calcaneus) forms the heel of one foot.
Skin, blood vessels, and nerves give the foot its shape and strength for every step you take, including the ability to control the foot’s many different movements.
Did you know?
Your heel bone receives up to four times your body weight with every step you take. Imagine that!
Shin bone (tibia)
Feel the long bone on the inside of your leg below your knee.
That’s your shin bone (or tibia) – the main bone of your lower leg that runs along the inside of your leg, linking your knee to your foot.
The fibula is the smaller of the two long bones in your lower leg, and runs from your knee to the ankle along the outside of your lower leg. It supports your ankle.
Did you know?
Heard of shin splints – the pain around your shin bone? These are one of the most common causes of sport injuries and can happen when you don’t train properly.
Kneecap (patella)
Your kneecap (patella) is a thick, triangular shaped bone. It covers and protects your knee joint from injuries.
Your kneecap is one of three bones, along with the tibia (shin bone) and femur (thigh bone), that make up the knee joint.
Did you know?
Your knee joint is the largest joint in your whole body.
Thigh bone (femur)
Your thigh bone is the biggest bone in your body.
It stretches from your pelvis to your knee, and helps to carry your body weight.
It’s the longest bone in the human body and is one of the strongest and heaviest.
Did you know?
When you’re a baby, you have more than 300 bones. But by the time you’re an adult you’ll only have 206 because some of your bones join together as you grow.
Hips (pelvis)
Place your hands on your hips and feel the hard bone. That’s your bowl-shaped pelvis, which protects part of your digestive, reproductive and bladder system.
Your pelvis is attached to three types of bones – part of your backbone and your hip bones. It supports your body weight helps you stand in an upright position.
Did you know?
The opening in the middle of the female pelvis is wider than in men. This is to allow enough room for a baby’s head to squeeze through during birth.
Breast bone (sternum)
The sternum or breastbone is the flat bone at the front of your chest that is connected to some of your ribs, helping to form your rib cage.
The sternum acts like a shield to protect your heart and lungs from injury.
Did you know?
Your breast bone is about 15cm tall, covering about half the length of your ribs.
Radius and ulna
They sound like planets but they are not! Your elbow joint is made up of three arm bones.
One of these bones is called the radius, which is the bone that runs from the elbow to the thumb side of your wrist.
The other two bones that make up your arm joint are called the ulna and humerus. The ulna is the bone that sits next to your radius and runs from your elbow to the little-finger side of the wrist. The humerus is your upper arm joint.
Did you know?
The length from your elbow to your wrist is the same as the length of your foot!
Upper arm bone (humerus)
Ever wondered where the name ‘funny bone’ came from?
Humerus is the proper name of your upper arm bone. This is the long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow.
Did you know?
The bones in your body are not white. They actually vary in colour from light brown to beige. Bones often appear whiter than they are because they have been cleaned.
Ribs
Ever wondered how many ribs you have on your body?
Shut your eyes and start counting and then see if you’ve guessed right.
You have 12 pairs of curved ribs which make up your ribcage, and they protect all the organs inside your chest. They are also attached to your spine (also called the backbone).
Did you know?
Violent coughing can fracture (break) a rib but this usually only affects adults or people with weak bones!
Spine
Your spine is like a daisy chain. It is made up of a long chain of 26 bones called vertebrae that run down the middle of your back. Without a spine to hold us upright our bodies would slump forwards.
If you view your spine sideways it is like an S-shaped, which makes it springy so it can cope with all the different movements and positions that you do above your legs.
Did you know?
Children have 33 vertebrae. As you grow, some of the vertebrae at the bottom of your spine will join together reducing the number to 26.
Shoulder blades
Your shoulder is made up of your shoulder blade (scapula) and your collarbone (clavicle).
The scapula, or shoulder blade, is a wide, flat bone that sits behind the rib cage. Together with the collarbone they form the part of your shoulder that connects your arm to your body.
The shoulder joint is very flexible and can move in lots of different directions. It is held together by lots of muscles. The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint and is the most freely moving joint of the body – it can move in lots of different directions.
Did you know?
Your shoulder joint is able to move in more directions than any other joint in your body. Just swing your shoulder around in a full circle and see how easy it is!
Teeth
Imagine trying to eat your food without teeth? Not an easy thing to do!
When you chew food your teeth have an important job. They help to crush the food to make it easier to swallow and digest in your body.
Every tooth has a root that attaches the tooth to your jawbone. The bit that we see is the crown, which is made up of hard, white enamel. Below the enamel are other bone-like bits that help to shape the tooth and give you feeling in your teeth.
What is a cavity?
If food gets stuck in your mouth for too long, bacteria in your mouth will start to feed on it. While doing this the bacteria can also attack the enamel on your tooth, giving you toothache and a hole in your tooth.
If this happens you will have to go to the dentist to get a filling. But, if you want to cut down on your trips to the dentist make sure you brush your teeth well twice a day, and cut down on eating sweet foods, which we all know can damage the enamel on our teeth.
So it’s important to keep your teeth clean!
Did you know?
The hard white enamel on the outside of your teeth is the hardest part of your body.
Skull
Tap your skull and feel how hard it is. That’s because it’s made up of bones fused (joined) together and has the very important job of protecting your brain.
Your skull also supports your face and mouth muscles.
When you are a baby your skull is very soft, and gets harder in the first few months of your life. The skull at the front of your head – that covers and protects your brain – is called the cranium. You also have fourteen bones at the front part of your skull that shape your whole face (including your nose bones and jaw).
The shape of our skull will decide what a person will look like. That’s why experts can use a skull of a dead person to help them find out what that person might have looked like when they were alive.
Did you know?
There are 30 different bones in the skull.
Ears
Ears are not just the squidgy flaps on each side of your head. They’re way more complicated! As well as allowing you to hear, they also help your balance, and stop you from falling over!
The parts you can see are called the outer ears. They’re like goal posts, collecting lots of sounds. These go into the middle ear. Here you’ll find your eardrum and three ossicles (tiny bones), plus the hammer. The hammer’s not the kind you’ll find in the garage at home. It’s actually another small bone – you’ve also got an anvil, incus and stirrup in each ear! This part of the ear transfers the vibrations caused by sounds into the deepest part of the ear.
The inner ear’s where the vibrations hit a curly tube, called the cochlea. This is filled with a special liquid that helps turn the vibrations into signals that your brain can understand.
Did you know?
Ear wax is made in the ear to protect the inside of the ear from dust and dirt. It’s smell stops creepy crawlies and insects from entering the ear!
Bones and joints
The shape of your body comes from your bones. That’s because everything is held inside your skeleton, which is made up of them.
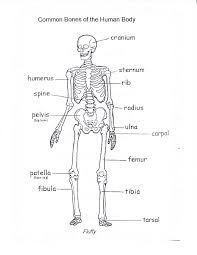
You won’t normally see the outside of a bone, but if you could, you’d see the cortical. This is the smooth but very strong part. Underneath you’ll find lots of layers of cancellous bone, which is like a hard sponge. In some bones, you’ll also find bone marrow. This is a thick, sticky substance that makes blood cells. Most of the calcium in your body is in your bones and teeth.
A joint is the area where two or more bones meet. Some of your joints will only bend in one direction, while others can move in lots of different directions such as your hip and shoulder joint.
Did you know?
There are more than 200 bones in your body, and your feet are made up of one quarter of all the bones in your body. Wow!
Hair
What’s the difference between your hair, your nails and the top layer of your skin?
Actually, not that much! They’re all made from the same stuff – keratin. They all work in different ways in helping to protect your body.
Hair helps to keep you warm, and stops things from getting in your eyes. Each hair is born in a tiny hole called a follicle.
Did you know?
Our eyes are always the same size but our ears and nose never stop growing!
Nerves
You have nerves all over your body which have a very important job. They carry messages (signals) from your brain to all the different parts of your body, that allow us to do different things.
The whole network of nerves in your body is called your nervous system.
Your nervous system allows you to do many things – to store information, send out instructions to your body, have feelings, to think and breathe without thinking and much more.
They are busy working around the clock to allow your body to do lots of different things at the same time.
Did you know?
Nerve messages whizzing from our brain can travel as fast as 170 miles per hour!
Muscles
Everyone’s got muscles – at least 600 of them!
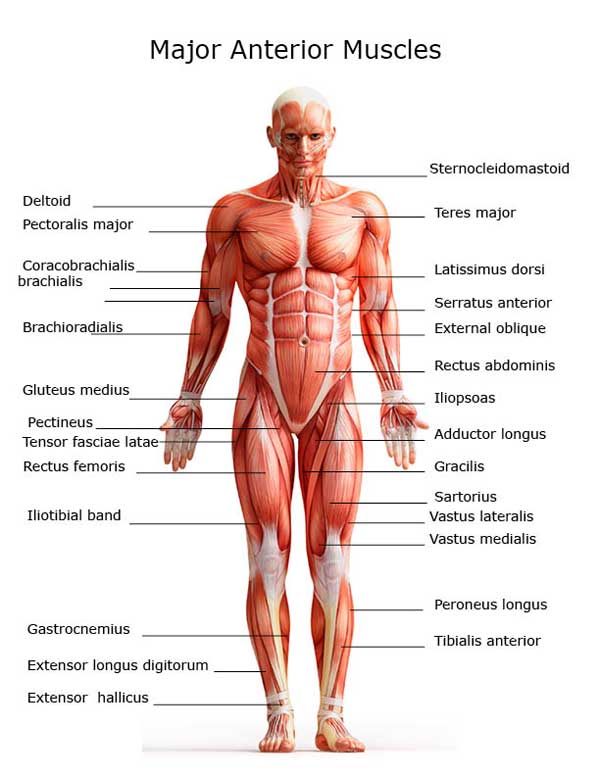
Some are easy to find like your arm muscles – but others are hidden away, such as in your heart. Your muscles are all very flexible, which allows them to move about.
That’s because they all do something – some help your heart to work, others allow you to walk or run.
Muscles work by tightening and then relaxing.
For example, when the muscle in your upper arm (called the bicep) tightens, it pulls up your lower arm.
Others work all the time without you having to do any work, like your heart muscle which pumps blood around your body, and the muscles around your lungs that make you breathe.
Did you know?
The most important muscle in your body is your heart, which is in charge of pumping blood around your body.
Skin
You can’t actually see most of your body – it’s hidden behind skin. Skin protects everything inside you.
But, it also helps you to feel things, through your nervous system, which controls your senses. You have two main layers of skin.
The outer layer is called the epidermis, and is covered in dead cells. The layer below is where your new cells are and is called the dermis.
Another coating of protein called keratin covers the epidermis This is partly because your skin is so important.
It is strong, but it can damage very easily. When you cut yourself (ouch !) the damaged skin will repair itself. This can take a few days, if it’s a small cut. But, more serious cuts can take a lot longer to get better.
Did you know?
The color of your skin depends on how much melanin (dark coloring) you have in your skin. Pale-skinned people have less melanin in their skin than dark-skinned people. Melanin helps to protect our skin from sunburn.
Nails
Your nails, your hair and the top layer of your skin are all made from the same stuff – keratin. In their own ways, they all protect your body.
Nails are made up of dead cells, which is why it does not hurt when you cut your nails. They help to look after your fingers and toes. They are also very useful in other ways, such as helping you to pick up small things or scratch different parts of your body.
Did you know?
Our nails grow about a millimetre every ten days and grow faster in summer than in winter.
Blood
Blood is a red liquid that travels to all parts of your body. It works like a highway, carrying cells around the body.
It’s made up of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, which float in a liquid called plasma. Blood is important for a lot of reasons. It moves oxygen, nutrients and water around your body, and it helps you to fight infections. It also picks up the body’s waste products and carries them to the lungs and kidneys, where they are released from the body.
Blood is carried around in veins and arteries. These are tiny tubes that run throughout your body and are also called blood vessels. Not everyone has the same type of blood.
Did you know?
There are four main types of blood and each person will have a different type of blood in their body. These are called: A, B, AB and O.
Arteries and veins
Arteries and veins are the two main kinds of blood vessels that carry your blood around the body.
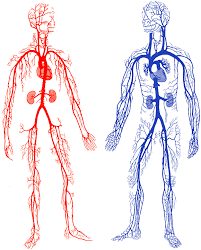
But, they both do different jobs. Your arteries carry blood filled with oxygen, and your veins carry blood filled with carbon dioxide and other waste materials that the body gets rid of. When we breathe in, our lungs fill with up with oxygen that keeps us alive. Then, when we breathe out, the air that we let out contains carbon dioxide, which we get rid of.
Did you know?
It takes about a minute for blood to travel all the way from your heart to your toes and back again!
Kidneys
Kidneys are shaped like beans and work in pairs but you can live (survive) with just the one.
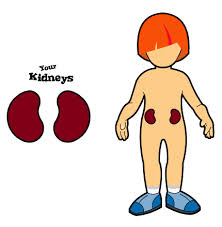
They’re hidden away at the side of your body, just behind your rib cage.
Their job is to keep your blood clean, taking out any nasty waste, that is turned into a liquid called urine. Urine stays in your bladder and is released when you pass urine. Your kidneys also keep a check on your hormones. Hormones are a chemical that the body makes to help you to grow.
Did you know?
If one of your kidneys stops working the other kidney does all the work, which means that you can survive on one kidney!
Digestive system
Ever wanted to know what happens to your food when you pop it in your mouth?
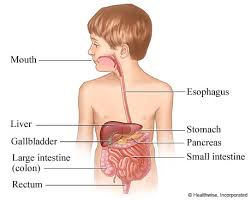
Your body needs the food to give you energy and to help you grow. To do this it first needs to break the food down in a process called digestion.
When food enters your mouth your teeth break it up, then your tongue and spit (saliva) help to get the food ready for you to swallow it.
Then it’s taken down a tube called the oesophagus, which goes down to your stomach (tummy). Special juices (gastric juices) turn your food into a soft mixture.
This is taken into the small intestine, which isn’t actually that small. Although it’s only a couple of centimetres wide, it’s usually about seven metres long (the height of a house!)
The slft mixture is broken down even more by your pancreas and liver. That’s when it’s finally ready to be used by your body. The large intestine can then start to get rid of the bits of your food that your body doesn’t need through the rectum (bottom).
Did you know?
It can take hours or even days for food to work its way through your digestive system.
Liver
Your liver is one of the biggest and busiest organ in your body. It has hundreds of different jobs to do.
For example, it makes a substance called bile, which is important because it helps to break the food down in your body. It also helps to work out what your body needs from food – the nutrients – and if you’ve got too much of something, it can store it up!
Did you know?
Your liver is your biggest internal body organ and weighs 1.5kg (3.3 lb)!
Heart
Your heart is actually a fist-sized muscle, like your arm or leg muscles, but it does a very different job.
It doesn’t make you move, but it does move blood around your body. It has an important job because blood carries oxygen and nutrients around your body.
The heart works like a car engine, taking blood in on the right side and pumping it up to your lungs. The other side takes blood back from your lungs and around the rest of your body. Your heart is pumping all of the time – that’s when it beats, usually about once every second.
Did you know?
The human heart will pump 160 million litres of blood in an average lifetime!
Lungs
Breathe deeply. Then you’ll really feel your lungs at work – they’re like two plastic bags that fill up with air when we breathe in. The air has oxygen in it that we need to stay alive.
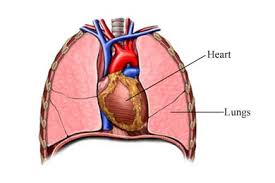
The lungs help you to breath in new air, and get rid of old air when we breathe out. The air that we breathe out has carbon dioxide in it that we want to get rid of. Our lungs are one of the biggest organs you have and they’re very important – they even help you to talk and sing!
Did you know?
We breathe in (inhale) air about 20 times in a minute – that’s a lot of air!
Tongue
Stick your tongue out and look at it in the mirror. Have you ever noticed all the tiny bumps that it is covered in?
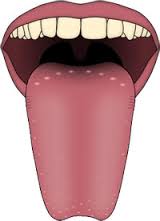
These are called taste buds and they tell you whether your food is sour, sweet, salty or bitter.
That’s because there are taste buds in different parts of your tongue that can understand all the different tastes. But, that’s not the only job that your tongue does. It also helps us to form words, and is therefore a very important organ in helping us to speak.
Did you know?
Your tongue has around 10,000 taste buds that are sensitive to different tastes.
Tonsils
Your tonsils are like soldiers. They guard the opening into your throat and help to fight dangerous bacteria that enters into your mouth by air and food.
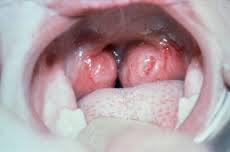
Tonsils are on both sides of your throat, at the back of your mouth, and are easy to see.
When you’re very young, your tonsils will grow, because you need extra help fighting infection but they shrink by the time you go to school, disappearing almost completely by the time you reach adulthood.
In some young adults and teens, the tonsils become infected many times with bacteria and viruses, which make them swell and become painful. Removing the tonsils stops this from happening.
Did you know?
As you get older your tonsils begin to shrink. They are then probably no longer as useful. This is in protecting against the germs that cause disease.
Nose
What allows us to smell? Our nose of course!
When you breathe in the smells in the air enter your nose and help you to taste things. The air is sucked up by the mucus (snot!) inside your nose.
Nerve endings in the back of your nose that work like smell detectors take in the smell, and together with the sense of taste, send nerve messages to your brain, allowing you to taste different flavors.
Not being able to smell is like having a cold, when your nose gets all blocked up, and you can’t really taste your food.
Did you know?
Our nose never stops growing until the day we die!
Eyes
Have you ever looked at your eyes in the mirror? They look like squidgy white balls, but they’re a lot more complicated than that.
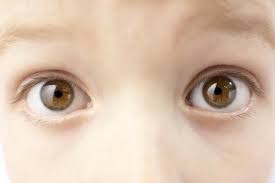
They work a lot like a video camera – taking in colours and shapes and then turning them into information that your brain can understand.
The most noticeable part of your eyes (the white bits!) is called the sclera. Its job is to protect your eyes (along with your eyelids). Look at them closely and you’ll see lots of tiny lines – these are blood vessels, taking blood into your eyes.
Under this, you’ll find (but won’t see) the cornea. It’s a clear substance that works like a lens, helping your eyes to focus. The iris (that’s the coloured part) allow enough light into your eyes. And, if it’s bright, they’ll stop too much coming in!
Did you know?
Our eyes are always the same size but our ears and nose never stop growing!
Brain
It’s a-maze-ing! Your brain looks like a grey, spongy maze. It may look a bit weird, but it’s actually more complicated than the most powerful computer.

The brain is the most important part of your nervous system. It controls your breathing, heart rate and digestion. It is also the area where we do our thinking, feeling and learning. The cerebrum is the main part of your brain that does the thinking, and is split into two – one half on each side of your head.
The left side of your brain looks after the right side of your body. And, the right side of your brain looks after the left side of your body! There are lots more parts to the brain. One of the most important parts is the brain stem. This connects the rest of your brain to your body, through your spinal cord, which runs through your neck and back.
Did you know?
Your brain can weigh more than a kilogram (three pounds), filling most of the area inside your head!
Improving your diet
A healthy diet is a balanced diet. You can improve your diet by looking at the food groups and make sure you’re getting the best of them. As well as avoiding the worst!
You could also tell whoever shops and cooks for you about the tips in this section. Or you could even print off the page for them so they have it to hand. They might thank you for helping them to get healthy too!
Milk and dairy products
Milk and dairy products are generally healthy foods, but they are high in saturated fat. Saturated fat is bad for your heart. So it’s best not to have too much of it. An answer to this is to look for reduced-fat or low-fat dairy products. These products still contain the same amount of protein, vitamins and minerals. They just contain less fat!
Healthy dairy tips
- Swap full-fat milk for semi-skimmed milk.
- Pick low-fat yoghurts.
- Look for reduced-fat cheese.
- Have just a scraping of butter or margarine on your bread.
- Use low fat natural yoghurt instead of cream.
Fruit and vegetables
It might be boring to hear… but you should eat at least five portions of fruit and vegetables every day. Fruit is important for the diet and a good source of vitamins, minerals and fiber. If you’re not keen on certain fruit and veg, try them again or mix them with other foods like yoghurt or cheese to help them go down!
Easy ways to get your five a day
- Have a glass of fruit juice or a fruit smoothie.
- Add dried fruit to your porridge and cereals.
- Eat one banana a day.
- Add fresh, tinned or dried fruit to yoghurt.
- Feast on crunchy carrot and celery sticks with dips.
- Make tomato salsa for fun and use as a dip.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates should be the main part of every meal. Wholegrain carbohydrates are higher in fiber. These are ones like wholemeal bread and pasta, brown rice, bran flakes, porridge and rye crispbread. Refined carbohydrates have had the high fiber bits removed by machinery. These include white rice, white bread, noodles, white pasta and sugary breakfast cereals.
Meat, fish and vegetable protein
Meat is good for you because it has nutrients including protein, iron, zinc and B vitamins. But beware! Although some lean meats are lower in fat, like chicken and turkey, others contain a lot of saturated fat. The healthiest way to eat meat is to have it lean and cut off all the fat and skin.
Experts say that we should have fish at least twice a week. One of these meals should contain oily fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines or fresh tuna. These contain omega 3 fatty acids, a very important part of a healthy diet. These help you to have a healthy heart!
If you don’t eat meat and fish then vegetable protein can give you of iron, zinc and the B vitamins along with extra fiber. To get enough of these nutrients eat 3 portions a day. Try to have a variety of beans, lentils, daal and peas. Vegetarian sources of omega 3s are: flaxseeds, walnuts and green leafy vegetables.
Tips for less fat in this food group
- Don’t eat the skin or fat on chicken or other meats.
- Try not to stuff yourself with sausages, salami, beef burgers and meat pies, these are high in fat as well as salt.
- Cook meat by baking, roasting or grilling.
- White meats are lower in fat than dark or red meats.
- Beans and other pulses are brilliant as they are low in fat and high in protein. Try them instead of meat in different dishes.
- Bake, grill or steam fish – it tastes better than if you fry it!
Fats
There are some fats, which are good for you. These are unsaturated fats. The other type of fat is saturated fat, which is bad for you.
Saturated fat
This is nearly always animal fat and is often solid at room temperature. It’s found in full-fat dairy products and things made with these ingredients like cakes, biscuits, chocolate and pies. It’s the white stuff you see on red meat. Eating a lot of this type of fat can cause heart disease.
Unsaturated fat
This usually comes from vegetables and nuts and can be polyunsaturated (like corn oil) or monounsaturated (like olive oil). This fat is liquid at room temperature and you can use margarines containing these fats instead of using butter.
Eating tips for teenagers
You’ve probably heard people saying it’s important to eat a good and balanced diet. It’s essential for helping you become a strong and healthy adult.
Five a day
We should all be eating at least five portions of fruit and vegetables a day as part of a healthy lifestyle.
Try and get into the routine of eating a fruit snack in the morning, plus a helping of veg or salad and a piece of fruit for both lunch and your evening meal.
You could even try tinned fruit, as long as it’s in juice and not syrup, or dried fruit like apricots, sultanas, raisins, apples and pears.
More healthy snacks
Try replacing snacks with a high sugar/fat/salt content with healthier options, like fruit, oatcakes and breadsticks. You don’t have to cut out bad snacks completely, just eat them occasionally instead of all the time. Get your sweet fix from fruits like banana or strawberries instead of chocolate and sweets.
Fewer fizzy drinks
Swap fizzy drinks / aerated drinks for lots of water. Or, try a glass of fruit juice as a substitute instead (but just one glass a day). Fruit juice counts towards your five a day, and will help satisfy your cravings for sweet things.
Variety of foods
The key to healthy eating is to consume a variety of foods from across the food groups. The perfect balance is to get plenty of starchy carbohydrates, fruit and vegetables, enough milk, dairy and protein foods, but to go easy on the fats and sugars.
One step at a time
Getting into healthy habits at an early age can have huge benefits right through your life. It can protect you against disease; keep you trim and stop you living off junk food when you leave home.
The rewards from a few simple changes to your diet can be massive. Take it one step at a time and try to have fun with it – you shouldn’t see healthy eating as a problem.
Drinking
You need to drink to keep healthy and keep growing. It helps your brain and body work properly, as well as your digestion.
The amount of water you need to have depends on your age, weight, how much exercise you do and how warm it is. You’ll need more in the summer or when it is really hot.
So, it’s important to keep drinking throughout the day. But what should you drink? And how much?
Well it’s easy to work out what not to drink! Kids who have lots of sugary drinks (fizzy drinks, aerated waters and squash) are more likely to put on weight and to be overweight.
The best drinks to have are water and semi-skimmed milk. These don’t contain added sugar that can damage teeth. And milk contains important vitamins and minerals, like calcium.
Fruit juice contains lots of sugar. Eating the whole fruit is often better because then you get the fibre with it. This makes you feel full up. Juice is healthy, but one glass a day is enough. It’s also a good idea to have this at mealtimes for the sake of your teeth. Either this or you can water it down if you like. You can do the same thing with squash. One glass of pure fruit juice counts as one portion of your fruit and vegetables a day. Two glasses does not mean two portions though. This is because you are not getting the fiber.
How much should I drink?
Aim to drink 6-8 glasses of fluid per day. Your urine is good at showing if you should be drinking more. If it’s dark yellow then you need to drink more – your urine should be light yellow. Remember to drink more if you are doing exercise. This will stop you from getting dehydrated (i.e. your body does not have enough water).
Get active!
You may find that television takes up a lot of your time. Many kids spend lots of time watching TV. It’s the same with computer games and the Internet.
All the time you’re doing this you are not active. You would actually burn more energy if you were reading a book!
It’s also tempting to sit and eat snacks while you watch your favorite programmes. Especially when you keep seeing adverts for unhealthy drinks and snacks. The chances are the foods you’ll be snacking on are crisps, biscuits, cakes and fizzy drinks!
How to stop being a telly-tubby
- Get out of the house and go and get some exercise!
- Pick two or three favorite programmes and only watch these.
- Don’t keep the television switched on in the background.
- Find a new hobby you can do at home such as drawing or painting.
- Don’t have a television or computer in your bedroom.
- Pull your sports stuff out of the cupboard.
- Put some music on and have a dance about or try karaoke!
- Ask your parents if you can learn a musical instrument.
Remember, doing any physical activity is better than sitting in front of a television or computer. It will burn more energy and means it’s not so bad when you have the odd ice cream or bag of sweets.
Did you know?
- Almost half of children spend more than three hours a day watching television or playing computer games.
- Children eat more when they are watching television than at any other time. So watching less TV stops kids from putting on weight.
Exercise for teenagers
You might find that you spend a lot of time watching TV – many young people do.
It’s the same with playing computer games and browsing the internet. This might be how you like to spend your leisure time. But while it’s fine to do these things and spend time relaxing once in a while, the problem is you’re not being active.
Why exercise?
If you’re inactive as a young person, you’re more likely to be inactive as an adult. This puts you at risk of developing life-threatening conditions like heart disease and cancer.
Research also shows that regular physical activity can boost our self esteem, mood and sleep quality, making us less prone to stress, depression and, in the longer term, dementia. In short, doing regular exercise is good for our bodies and minds.
How much exercise?
Health experts recommend you do at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity every day – do more than this if you can and want to.
Moderate-intensity activity
Things like:
- bike riding
- briskly walking
- playing frisbee in the park
- martial arts
Anything that means you’re working hard enough to raise your heart rate – so you breathe harder and begin to sweat – but are still able to talk.
High-intensity and resistance exercise
It’s recommended that you do higher intensity and resistance activities three days a week because these will help strengthen your muscles and bones.
Things like:
- gymnastics
- tennis
- skipping
- sit ups and push ups
It’s important to find an activity you enjoy so you don’t find it boring – it means you’ll be more likely to stick at it. Why not join a sports team or exercise with family or friends?
Protect yourself
Whatever exercise you choose, you’ll need to use the right protective equipment – including footwear. This is to reduce your risk of injury.
If you decide to use weights as part of your resistance training, make sure you’re supervised by a trained adult. This is so you use the right equipment and to avoid injuries to your growing muscles and joints.
How much exercise?
Kids and young people should do between 30 and 60 minutes of exercise every day.
This could be brisk walking, swimming, cycling or simply running around in the playground. Your PE teacher will be able to help you decide how much exercise you need to do.
Exercise like dancing and gymnastics once or twice a week are good for keeping bones healthy. They also strengthen your muscles and are good for flexibility.
Team sports are a fun way to exercise. They help you to get outside with your friends. There’s also the chance to make new friends! Team sports also help your co-ordination, balance and ball skills. If you don’t like team sports you can always try other activities like roller-blading, skateboarding or martial arts.
Try to do lots of different types of exercise. This way you are less likely to get bored!
Remember that you can get fit even if you are overweight or obese. You don’t have to be naturally ‘sporty’. It doesn’t matter how much you weigh, exercise will improve your health.
What’s to gain?
Exercise is very good for your body and mind. The most important thing is that it burns up extra energy. This extra energy is normally stored as fat. So if you’re exercising every day, this won’t go on as extra weight.
Being active also keeps your muscles flexible, works out your heart and lungs and gets the blood going to the brain! It helps you to digest your food better and helps you to sleep better.
Another big benefit of exercise is that it makes you feel good! This is because when your body is active it makes chemicals called endorphins.
These chemicals help your mood and give you a feeling of well-being. Chocolate also produces endorphins, which is why you can feel good after munching on a bar.
Just think how much better it would be to get the feeling from doing something healthy instead!
So exercise makes you feel good about yourself. This puts you on the path to greater self-esteem and super confidence!
Benefit of exercise
- Keeps your weight under control.
- Lowers high blood pressure.
- Reduces risk of heart disease.
- Helps you concentrate at school.
- Reduces chances of type II diabetes.
- Boosts bone health.
- Lowers risk of cancer.
- Helps you to make new friends.
- Boosts your mood.
Exercise centre
Sometimes the word ‘exercise’ can make you feel tired just thinking about it! But exercise doesn’t have to be a chore. Often, if you avoid exercise the more difficult it seems. It can seem even harder if you’re overweight.
But the more unfit you are, the more weight you put on, and the less you want to exercise… it becomes a vicious circle!
When you are active you burn more energy. Your body then starts to use up its fat stores. It also starts to build muscle tissue, and this increases your metabolism. (Your metabolism is the speed at which your body burns calories.)
This improves your fitness and helps to keep your weight steady.
So where do I start?
When you’re unfit, suddenly doing a lot of exercise can leave you feeling stiff and sore. This is why you have to be careful when you first start out.
The best way is to start slowly. Do a little bit more each time so that your body gets used to it. It’s also a good idea to do some stretches first. Stretching stops you putting a strain on your muscles.
This way, you won’t feel uncomfortable while you’re exercising. And hopefully you won’t feel sore afterwards! If you do feel like it’s a struggle the first few times, don’t be put off. It’s true that each time you exercise it’s likely to be easier and you’ll enjoy it more.
Some people get scared when they think about exercise. They feel like they’re being asked to climb a mountain! It doesn’t have to be like this though. Lots of things are counted as exercise. Exercise includes anything that gets you a little bit out of breath. So things like:
- Walking, the simplest and cheapest form of exercise! Try walking to school instead of going in the car;
- Joining in with sports and games in breaks at school;
- Taking the stairs instead of the lazy lift!
- Getting off the bus a few stops early and walking the extra distance.
Food group fun
To be healthy it’s very important to eat a balanced diet. All foods can be put into one of five food groups. A balanced diet is made up of the five food groups.
1 Carbohydrates
This group contains starchy foods such as pasta, rice, oats, potatoes, noodles, yam, green bananas, sweet potato, millet, couscous, breads, breakfasts cereals, barley and rye.
Carbohydrates give us energy, calcium and B vitamins. Wholegrain ones give us lots of fibre to help keep the digestive system healthy. Many breakfast cereals also have extra iron. A healthy diet would include 3-5 servings of carbohydrate a day.
These portions should be spread throughout the day and eaten with every meal, including snacks.
One portion of carbohydrate is:
- One slice of bread, one roll or half a pizza.
- Six tablespoons of breakfast cereal or porridge.
- Four wholewheat crisp breads.
- Six tablespoons of pasta, rice, millet or couscous.
- Two small new potatoes.
- Two tablespoons mashed sweet potato.
2 Protein
This group contains meat, fish and eggs as well as vegetable protein, nuts, beans, peas, lentils, dahl, Quorn and soya. These foods give us protein, iron and some other minerals and vitamins. This helps the body to grow and repair itself. They are like building blocks for the body. Meat is a good source of iron. We should eat 2-3 servings of these every day.
One portion of meat or vegetable protein:
- Two slices of cold ham, turkey and chicken.
- One medium chicken breast.
- Two sausages.
- Three bacon rashers.
- One beefburger.
- One fillet of fish or fish steak.
- One small can of tuna, salmon, mackerel, sardines.
- Four fish fingers.
- One cup of cooked lentils or beans.
- Half a large can of beans, chickpeas or lentils.
- A 100g portion of Tofu or Quorn.
3 Milk and dairy products
This group contains milk, yoghurt, fromage frais, milkshakes, cheese – both hard cheese and soft cheese including soft cheese triangles. These foods contain protein and calcium and some vitamins like vitamin B12, vitamin A and vitamin D. Dairy products keep your bones and teeth healthy. The body absorbs the calcium in dairy foods easily. We should try and eat three servings of these a day.
One portion of milk and dairy products:
- One glass of milk.
- One pot of yoghurt or fromage frais.
- One matchbox size piece of cheese or two triangles.
- Half a tin of low-fat custard.
4 Fruit and vegetables
This group includes fresh as well as frozen, tinned, dried and juices of fruits and vegetables. Fruit and vegetables give you lots of vitamins and chemicals called antioxidants which keep you healthy. These can even stop you getting some cancers. They also contain fibre to keep your digestive system healthy. Because fruit and veg are low in calories and high in fibre (which keep kids feeling full) eating plenty will help control your weight It is important to eat a wide variety of fruit and vegetables. This way you get the whole range of all the important nutrients these foods give. You should eat at least five portions of fruit and vegetables a day.
One portion of fruit and vegetables:
- One apple, orange, pear or banana or similar sized fruit.
- Two smaller fruits such as plums, satsumas, kiwi fruit.
- A handful of very small fruits such as grapes, cherries or berries.
- Half to one tablespoon of dried fruits such as raisins, prunes or apricots.
- A slice of large fruit such as a piece of melon or a slice of pineapple.
- Three heaped tablespoons of raw, cooked, frozen or canned vegetables.
- A dessert bowl of salad.
5 Fats and sugars
This group contains butter, margarine, cooking oils, cream, salad dressings, chocolate, crisps, sugary soft drinks, sweets, jam, cakes, pudding, biscuits and pastries. These foods give us a lot of energy (calories) but not many nutrients.
Junk foods are often high in fat, sugar and salt. It’s important not to have too many foods from this group too often.




