INFORMATION AVAILABLE IN ENGLISH, GUJARATI AND HINDI
What are undescended testicles?
This is when the child’s testicles are not in their usual place in the scrotum. While your child is in the womb, the testicles are developing inside his abdomen. Towards the end of pregnancy, the testicles travel through a passage into the scrotum. Both testicles should be in the scrotum by the time the child is one year old. Generally, only one of the testicles is affected, but on rare occasions, both testicles fail to travel to the scrotum.
In some children, the testicles may be in the scrotum for much of the time but cannot be felt there because they naturally rise back into the body through fear or cold temperatures. This is called retractile testis. You can usually find this out by putting your child in a warm bath and checking whether you can feel both testicles. If this is the case, there is no cause for concern.
What are the symptoms of undescended testicles?
Usually, there will not be any symptoms at all, other than not being able to feel the testicles in the scrotum. Your child will not be in pain, and the undescended testicles will not interfere with any bodily function.
However, if one of the testicles becomes twisted (testicular torsion), this will be painful, either in the groin area or the abdomen, depending on the location of the testicle at the time.
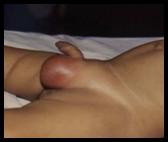
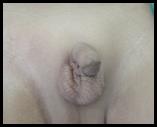 Right Undescended Testis
Right Undescended Testis
 Bilateral Undescended Testis (Hypoplastic Scrotum)
Bilateral Undescended Testis (Hypoplastic Scrotum)
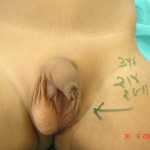 Left Undescended Testis
Left Undescended Testis
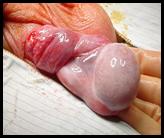
 Ectopic Testis (Pre Penile Testis)
Ectopic Testis (Pre Penile Testis)
Testicular Torsion
How are undescended testicles diagnosed?
The doctor will need to determine whether the testicles are truly undescended or whether they have slid back into the body temporarily. This is usually done by feeling the abdomen and the scrotum.
No investigations like ultrasound scan or CT Scan or MRI can determine the presence / absence or exact location of the testis. These investigations should be sparingly used for determination of the site of an undescended testicle.
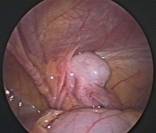
Laparoscopic view of undescended testis
What causes them?
On rare occasions, the testicle does not descend due to other problems with the testicles themselves or with the male hormones.
We do not know exactly why this happens, but it is not due to anything that happened during pregnancy.
How common are they?
This condition is more common in premature babies. 33 % of premature and 3 % of term children are born with undescended testis. The incidence of undescended testis at the age of 1 year is 1 %. Hence only 2 % of testicles descend up to the age of 1 year. The incidence of undescended testis in the adult population is 0.8%. These figures show that after the age of 1 year, there is hardly any decrease in the incidence of undescended testis.
How undescended testicles are treated and are there any alternatives?
The method of treatment depends on the suspected cause. However, whatever the cause, undescended testicles are best treated in early childhood latest by the first birthday of the child. Your child’s testicles will need treatment as they do not seem to mature properly if left in the abdomen. The amount of sperm and fertility levels seem lower in men who have had undescended testicles, and even lower if they were not treated early in childhood. This is because the testicles need to be a few degrees cooler than the rest of the body to produce sperm. It is also impossible for men with undescended testicles to check for testicular cancer, as the testicles cannot be felt in the abdomen. If the testicles remain in the abdomen, this also increases the risk of testicular torsion.
What is an orchidopexy?
This is an operation to bring the testicles down from the abdomen to their usual place in the scrotum. This is a short operation under general anaesthetic, lasting about 45 minutes. Occasionally, a child will need to stay in hospital overnight.
What does the operation involve?
Operation involves moving the testicle down into the scrotum, and close up the passage through which the testicle should have travelled, to stop the testicle moving back into your child’s abdomen. The testis is secured in the scrotum to ensure that it remains in place and develops in the normal way.
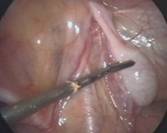
Operation can be done by the traditional open technique when the testis is palpable in the groins i.e. it has come out of the abdomen but not reached the scrotum. In cases where the testis has failed to come out of the abdomen key hole surgery or laparoscopy is used to determine the exact location of the testis in the abdomen along the course of its descent.
What happens afterwards?
The child will be reviewed a week after surgery. Follow up visits would be scheduled after 3, 6 and 12 months respectively.
What is the outlook for children with undescended testicles?
When the undescended testicles are treated in early childhood, the outlook is good. Your child will have normal fertility levels unless there were problems with the testicles themselves. In the event of the undescended testis being damaged prior to your realizing it / procuring treatment for the same, the child is left with on testicle. This however, should not affect your child’s fertility levels in later life to any great degree.
Operative videos of laparoscopy in undescended testis:
GUJARATI
વૃષણની ગોળી નીચે ન હોવી
અનડીસેન્ડેડ testis ત્રણ ટકા બાળકોમાં જાવા મળે છે. જા બાળક અધૂરા મહિને જન્મેલું હોય તો તેને અનડીસેન્ડેડ testis ની સંભાવના ૩૩% જેટલી વધારે હોય છે. બાળક એક વર્ષનું થાય ત્યાં સુધીમાં આ આંકડો ઘટીને ૧% જેટલો થઈ જાય છે. બાળક જ્યારે માઁ ના ગર્ભમાં હોય ત્યારે વૃષણની ગોળી બાળકના પેટમાં વિકાસ પામતી હોય છે. આ ગોળી ગર્ભનાં સાત થી નવ મહિના દરમિયાન બાળકના પેટમાંથી નીકળી અને વૃષણ કોથળીમાં આવી જાય છે, પરંતુ આ ગોળી બહાર આવવાના પ્રવાસ દરમિયાન અટકી જાય તો બાળકને જન્મ વખતે અનડીસેન્ડેડ ટેÂસ્ટસની ખોડ થાય છે. બાળકનો જન્મ થાય ત્યારે જ ડાક્ટર બંને ગોળી વૃષણ કોથળીમાં છે કે નહીં તેની તપાસ કરી લેતાં હોય છે.
સોનોગ્રાફી અથવા એમ.આર.આઈ. પણ ઘણીવાર ગોળી ક્યાં છે તેની સચોટ માહિતી આપવામાં નિષ્ફળ જતાં હોય છે.
વૃષણની ગોળીનું આૅપરેશન સામાન્ય રીતે બાળક છ મહિનાથી એક વર્ષની ઉંમરનું થાય એ દરમિયાન થઈ જવું જાઈએ. આ આૅપરેશનમાં જા મોડું થાય તો પેટની ગરમીથી વૃષણની ગોળીને નુકસાન થવાનો ભય રહે છે. જા ગોળીનું આૅપરેશન સચોટ અને સારી રીતે કરવામાં આવે તો બાળકને લગ્ન જીવનમાં કે બાળકો થવામાં બીજા બાળકોની સરખામણીમાં કોઈ જ તકલીફ પડતી નથી. વૃષણની ગોળી પેટની અંદર ફસાઈ ગઈ હોય તો તેવા કેસમાં બાળકને લેપ્રોસ્કોપી દ્વારા આૅપરેશન કરવાની જરૂર પડે છે. લેપ્રોસ્કોપીમાં ગોળી કઈ જગ્યાએ છે તે જાઈ શકાય છે અને સાથેજ લેપ્રોસ્કોપી દ્વારા તે ગોળી નીચે લાવી વૃષણ કોથળીમાં મૂકી શકાય છે. •
HINDI
अनवतीर्ण वृषण/अंडिसेंडेड टेस्टिस
टेस्टिस का विकास अंतःगर्भाशय काल में पेट की गुहा के भीतर होता है और बाद में ७वें और ९वे महीने के बीच अंतर्गर्भाशीय काल में वे अंडकोश में गिर जाते हैं। समय पर पैदा हुए ३% बालकों में और समयपूर्व पैदा हुए ३३% बालकों में अनडिसेंडेड टेस्टिस की समस्या पाई गई है। १ वर्ष की आयु तक इन बालकों में इस समस्या में १% तक की कमी पाई गई है। शिशु के जन्म के समय अंडकोश में दोनों टेस्टिस की जांच की जानी चाहिए।
अंडिसेंडेड टेस्टिस ९-१२ महीनों की आयु में स्वतः ही अंडकोश में गि्ार जाने के लिए जाने जाते है। हालाँकि, तब तक अगर वे अंडकोश में नहीं गि्ारते तो सर्जिकल हस्तक्षेप आवश्यक है। अनवतीर्ण वृषण का उपचार न किए जाने पर आगे चल कर आघात, मरोड़, ट्यूमर तथा शुक्राणुओं के कार्य में कमी जैसी जटिलताएं उœपन्न हो सकती है। अनवतीर्ण वृषण या तो पेट या अतिरिक्त पेट में हो सकते हैं। कोई भी जांच १००% सटीकता के साथ अंतर पेट के वृषण की उपस्थिति या अनुपस्थिति की पहचान नहीं कर सकता है। अतिरिक्त पेट वृषण के लिए, खुली सर्जरी की आवश्यकता होती है और अंतःप्राय वृषण के लिए, टेस्टिस की सटीक साइट और आकार की पहचान करने और अंडकोश में इसे लाने के लिए लैपरोस्कोपी अनिवार्य है। अंडिसेंडेड टेस्टिस की समस्या से ग्ा्रसित यदि कोई बालक बालचिकित्सा सर्जन के पास देरी से आता है तो टेस्टिस निकालना नहीं चाहिए, क्योंकि ऐसा करना बच्चे के लिए हानिकारक होगा। •